Grounding is a fundamental concept in electrical systems, designed to enhance safety and protect both people and equipment from electrical faults. With the increasing popularity of LED lights due to their energy efficiency and longevity, understanding whether or not to ground these lights is an important consideration for anyone involved in electrical installations. This article delves into the role of grounding in LED lighting systems, explores when grounding is necessary or optional, and provides guidance on ensuring safety and compliance.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding LED Lighting
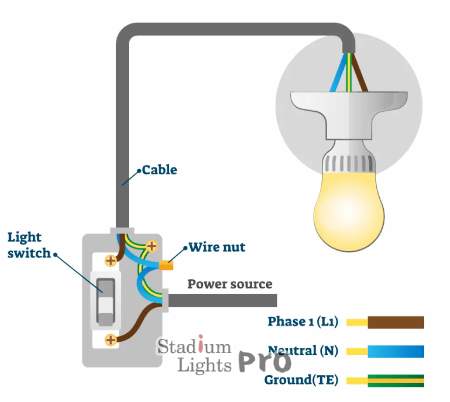
To address the grounding of LED lights, it is helpful to first understand how these lights operate and their inherent characteristics. LED (Light Emitting Diode) lights are based on semiconductor technology, which differs significantly from traditional incandescent or fluorescent lighting. An LED light consists of a diode that emits light when an electric current passes through it. This technology is known for its efficiency, producing more light per watt of electricity consumed compared to traditional bulbs.
LED lights come in various forms, including bulbs, strips, and integrated fixtures. Each type has its own design and application, but all LED lights share a common feature: they are designed to operate at low voltages, which generally reduces their risk of causing electrical hazards. However, their construction and installation can influence the necessity of grounding.
The Role of Grounding
Safety and Protection
Grounding serves several functions in electrical systems. Primarily, it provides a path for stray electrical currents to safely dissipate into the ground, thus preventing electrical shocks and protecting both people and devices. When an electrical fault occurs, such as a short circuit, the grounding system ensures that the fault current flows directly into the earth, rather than through a person or sensitive equipment.
Preventing Damage
In addition to safety, grounding helps to safeguard electrical components from damage caused by surges or faults. Electrical surges, which can result from lightning strikes or other disturbances, can damage sensitive components and cause malfunction. By grounding the system, these surges are directed away from the equipment, thereby minimizing the risk of damage and ensuring the longevity of the electrical components.
Compliance with Codes and Standards
Grounding also ensures that electrical systems comply with various codes and standards. These regulations are designed to promote safety and reliability in electrical installations. By following grounding requirements, installations meet the necessary safety criteria and are less likely to encounter legal or regulatory issues.
How Grounding Works
Connecting to the Earth
 In a typical electrical setup, grounding involves connecting the electrical system to the earth through a grounding wire. This wire creates a direct path for electricity to flow safely in the event of a fault. The grounding wire is connected to a grounding electrode, such as a metal rod driven into the ground, which provides a direct connection to the earth.
In a typical electrical setup, grounding involves connecting the electrical system to the earth through a grounding wire. This wire creates a direct path for electricity to flow safely in the event of a fault. The grounding wire is connected to a grounding electrode, such as a metal rod driven into the ground, which provides a direct connection to the earth.
Establishing Stability
By establishing this connection, grounding helps to maintain the system’s stability and safety. In normal operation, the grounding wire carries no current. However, in the event of a fault, it allows excess current to safely flow into the ground, thereby preventing potential hazards such as electric shocks or fires. This connection also helps to stabilize the electrical system by providing a reference point for the system’s voltage levels, which helps to prevent fluctuations and maintain consistent performance.
Grounding LED Lights
The question of whether grounding is necessary for LED lights involves several considerations. The design of LED lights typically incorporates features that reduce their reliance on grounding compared to traditional lighting options.
Are LED Lights Inherently Safe Without Grounding?
LED lights are generally safer than traditional lighting due to their low-voltage operation and the use of insulated components. Many LED lights are designed with double insulation, which means they are less likely to pose a risk of electric shock even if grounding is not provided. This double insulation comprises two layers of non-conductive material that protect the electrical components from coming into contact with the outer casing.
However, while LEDs themselves might be safe due to their construction, the need for grounding can still arise depending on the installation environment and the specific type of LED fixture used.
Grounding Requirements for LED Lights
Local electrical codes and regulations play a significant role in determining whether grounding is required for LED lights. These codes are developed to ensure that electrical systems are safe and reliable, and they often stipulate grounding requirements based on the type of installation and location of the lighting.
Manufacturers of LED lights may also provide specific recommendations regarding grounding. For example, integrated LED fixtures that include metal housings or components might require grounding to ensure safety and compliance with electrical standards. These recommendations are based on the design of the fixture and its installation environment.
Scenarios Where Grounding Is Required
Certain situations necessitate grounding for LED lights to ensure safety and compliance with electrical codes. One such scenario is when LED lights are installed in outdoor or damp locations. In these environments, grounding becomes crucial to prevent potential electric shocks and ensure that any moisture that might come into contact with the electrical components does not create hazardous conditions.
Another scenario where grounding is necessary is when using integrated LED fixtures that incorporate metal parts. Metal components can conduct electricity, making grounding important to prevent any risk of electric shock or damage to the fixture. Additionally, grounding helps to stabilize the electrical system and reduce the risk of electrical faults that could affect the performance of the LED lights.
When Grounding May Be Optional
While there are scenarios where grounding is required, there are also cases where it may be optional. The decision to ground LED lights can depend on the specific design and installation requirements.
LED Lights with Double Insulation
LED lights that feature double insulation are designed to provide an additional layer of protection against electrical faults. This design typically eliminates the need for grounding because the insulation effectively prevents any electrical current from reaching the outer casing. For these types of lights, grounding may not be necessary, but it is always a good practice to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and local electrical codes.
Low-Voltage LED Systems
Low-voltage LED systems, such as those using 12V or 24V power supplies, often operate with reduced risk compared to standard high-voltage systems. Because these systems are less likely to cause electric shocks or damage, grounding may be less critical. However, it is still important to ensure that all components are properly installed and meet safety standards. Following local codes and manufacturer guidelines will provide the best approach for handling low-voltage LED installations.
Specific Types of Installations
In certain types of installations, such as plug-in LED bulbs or fixtures designed for easy installation without complex wiring, grounding may be less of a concern. These systems are generally designed to be safe without the need for grounding, provided they are used as intended and in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Safety Considerations
When dealing with electrical installations, safety is always a primary concern. Even if grounding is optional in certain scenarios, it is crucial to consider potential risks and follow best practices to ensure safety.
Improper grounding can lead to several risks, including electric shocks, electrical fires, and damage to the LED lights themselves. To mitigate these risks, it is important to adhere to safety guidelines and regulations. This includes using properly rated components, following installation instructions, and consulting with a qualified electrician if there are any uncertainties about grounding requirements.
Best practices for ensuring electrical safety with LED lights involve more than just grounding. Proper installation, regular maintenance, and adherence to electrical codes are all important aspects of a safe and reliable lighting system. For complex or high-risk installations, seeking professional advice can help ensure that all safety considerations are addressed appropriately.
Conclusion
To make informed decisions about grounding LED lights, it is beneficial to refer to industry standards, manufacturer manuals, and local electrical codes. These resources provide valuable information on best practices and requirements for electrical installations. Additionally, consulting with electrical professionals can offer guidance tailored to specific situations and help ensure that all safety and compliance issues are effectively addressed.

